International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies
Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014
Cytochrome P450 3A and its role in metabolism of erythromycin by hepatic microsomes of Indian major carps, Labeo rohita (Ham.), Catla catla (Ham.) and Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.)
Author(s): Benoy Kishore Rai, Dawa Bhutia and Joydeb Pal
Abstract: Indian major carps, Labeo rohita, Catla catla and Cirrhinus mrigala were challenged intraperitoneally with a dose of erythromycin (50 mg kg-1 body weight) for 24 hrs, 48 hrs, 72 hrs and 96 hrs and hepatic microsomes were isolated. Cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) specific erythromycin N-demethylation activity (ERND) in the hepatic microsome was assayed. All three species showed positive reactions for CYP3A. In addition, CYP1A catalyzed ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity (EROD) and CYP2E catalyzed aniline-p-hydroxylation activity (APH) were also studied. It was concluded that the activity of CYP3A was induced in all the fishes while CYP1A and CYP2E activities were not significantly altered.
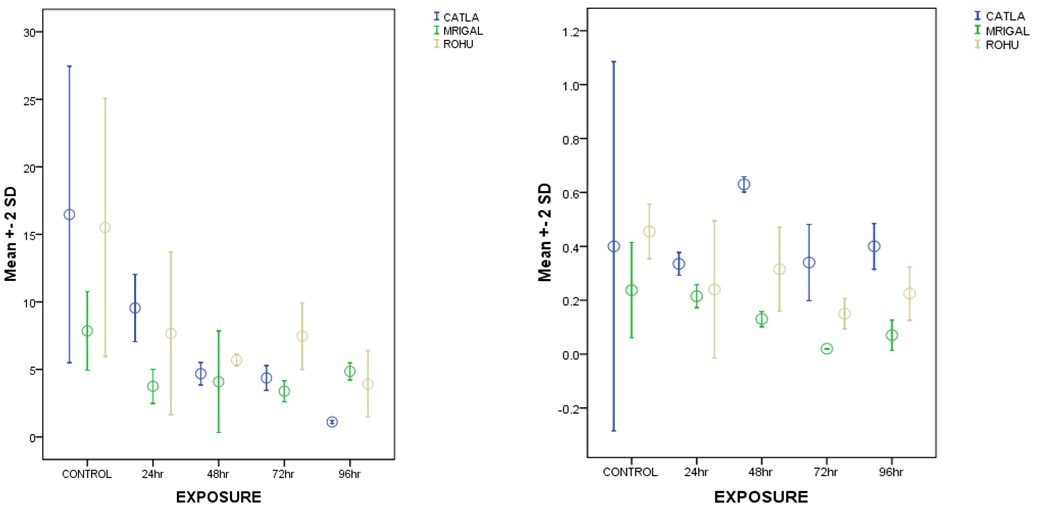
Fig: (a) EROD activity (pmol resorufin formed/min/mg Pr) and (b) APH activity (nmol p-aminophenol formed/min/mg Pr) in Indian major carps following exposure of erythromycin (50 mg/kg body weight).
Download Full Article: Click Here
Journal is Indexed and Abstracted in following Database(s).
    |
    |
       |

